CERN
Převzato z https://home.cern/.
What is CERN's mission?
At CERN, our work helps to uncover what the universe is made of and how it works. We do this by providing a unique range of particle accelerator facilities to researchers, to advance the boundaries of human knowledge. The Laboratory, established in 1954, has become a prime example of international collaboration. Our mission is to:
- provide a unique range of particle accelerator facilities that enable research at the forefront of human knowledge.
- perform world-class research in fundamental physics.
- unite people from all over the world to push the frontiers of science and technology, for the benefit of all.
Zdroj
CERN's accelerator complex
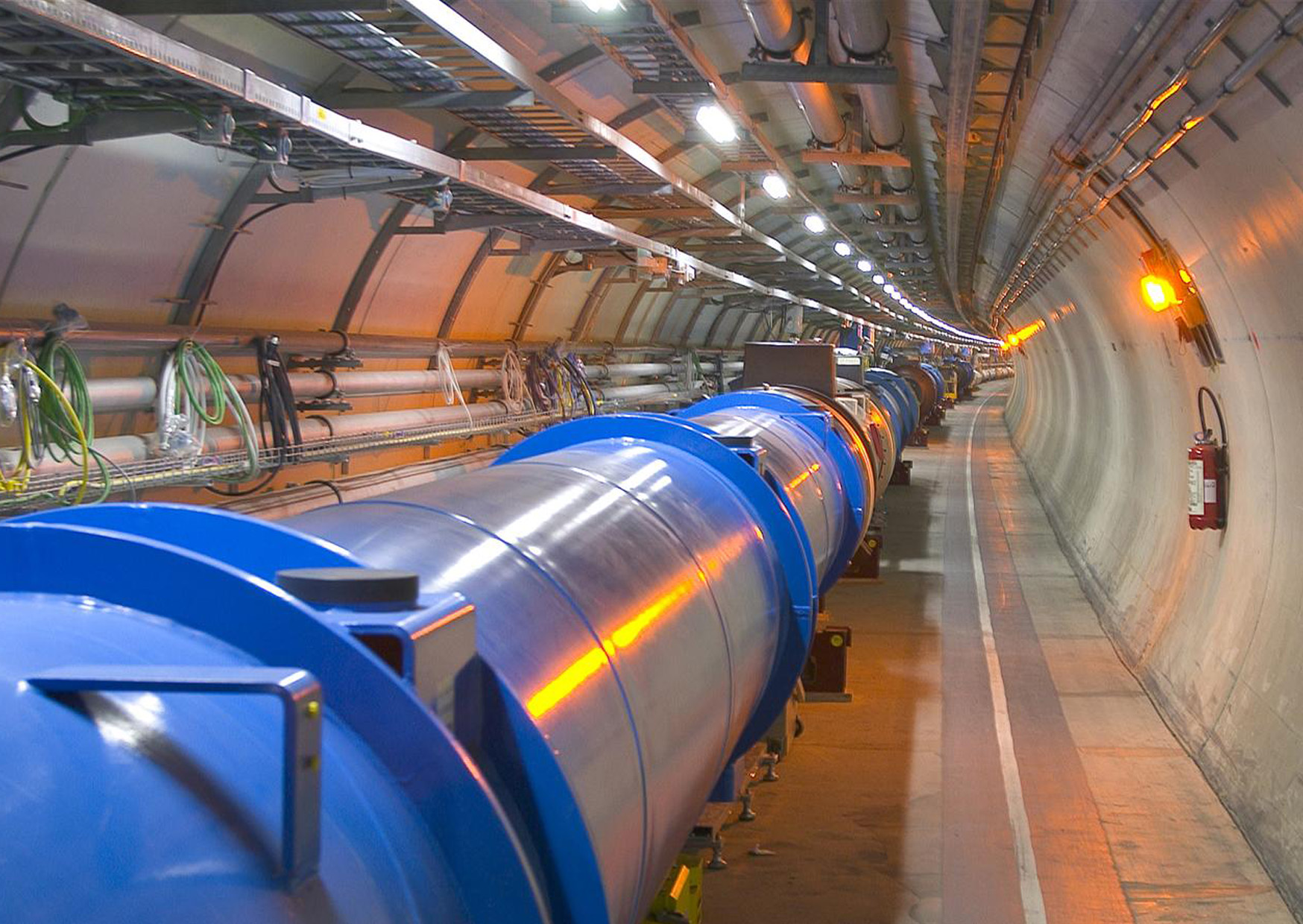
The accelerator complex at CERN is a succession of machines that accelerate particles to increasingly higher energies. Each machine boosts the energy of a beam of particles before injecting it into the next machine in the sequence. In the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) – the last element in this chain – particle beams are accelerated up to the record energy of 6.5 TeV per beam.
Linear accelerator 4 (Linac4) became the source of proton beams for the CERN accelerator complex in 2020. It accelerates negative hydrogen ions (H-, consisting of a hydrogen atom with an additional electron) to 160 MeV to prepare them to enter the Proton Synchrotron Booster (PSB). The ions are stripped of their two electrons during injection from Linac4 into the PSB, leaving only protons. These are accelerated to 2 GeV for injection into the Proton Synchrotron (PS), which pushes the beam up to 26 GeV. Protons are then sent to the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS), where they are accelerated up to 450 GeV.
The protons are finally transferred to the two beam pipes of the LHC. The beam in one pipe circulates clockwise while the beam in the other pipe circulates anticlockwise. It takes 4 minutes and 20 seconds to fill each LHC ring, and 20 minutes for the protons to reach their maximum energy of 6.5 TeV. Beams circulate for many hours inside the LHC beam pipes under normal operating conditions. The two beams are brought into collision inside four detectors – ALICE, ATLAS, CMS and LHCb – where the total energy at the collision point is equal to 13 TeV.
Protons are not the only particles accelerated in the LHC. Lead ions for the LHC start from a source of vaporised lead and enter Linac3 before being collected and accelerated in the Low Energy Ion Ring (LEIR). They then follow the same route to maximum energy as the protons.
CERN overview animation
https://videos.cern.ch/record/2020780

Zdroj
Otázky
Otázky:
- Co je to CERN?
- Co a proč v CERNu zkoumají?
- Popište, jak se v CERNu vyrábějí urychlené protony. Nakreslete schéma řetězce urychlovačů.
- Na internetu vyhledejte, jak na tomto projektu participuje Česká republika.

